Future-Oriented STEAM Education: Nurturing Tomorrow’s Innovators
Navigating Tomorrow: The Essence of Future-Oriented STEAM Education
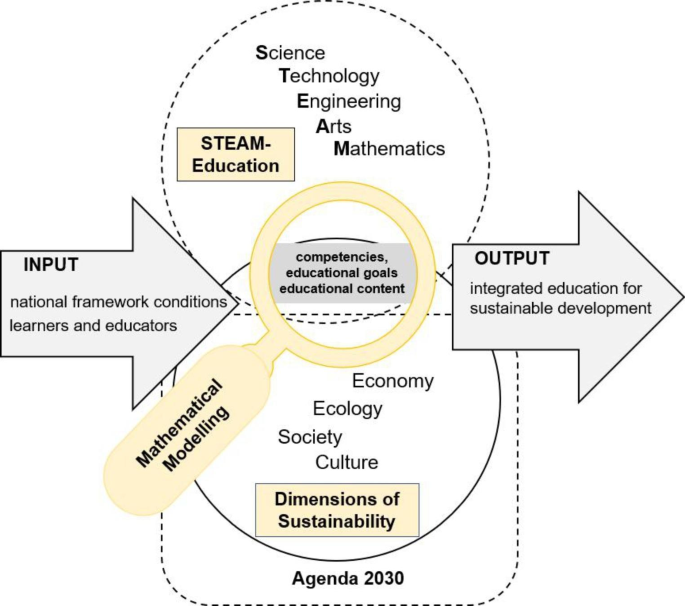
In the fast-paced landscape of education, Future-Oriented STEAM Education emerges as a beacon, steering students towards a horizon of innovation and adaptability. This dynamic approach not only equips learners with foundational knowledge in Science, Technology, Engineering, Arts, and Mathematics (STEAM) but also instills the mindset needed to thrive in the ever-evolving world.
Adapting to Technological Advancements:
Future-Oriented STEAM Education recognizes the paramount importance of technology in shaping the future. With an emphasis on cutting-edge technologies, students are exposed to coding, robotics, and other innovative tools. This prepares them to adapt seamlessly to the technological advancements that will define the future workforce.
Integrating Arts for Creativity and Expression:
Beyond the technical aspects, Future-Oriented STEAM Education integrates the arts to foster creativity and expression. By combining STEM disciplines with artistic endeavors, students develop a well-rounded skill set that includes not only analytical thinking but also creative problem-solving. This interdisciplinary approach prepares them for roles that demand both technical expertise and creative ingenuity.
Project-Based Learning for Real-World Application:
Future-Oriented STEAM Education emphasizes project-based learning, connecting theoretical knowledge with real-world application. Students engage in hands-on projects that mirror authentic challenges, allowing them to apply their skills in practical scenarios. This approach ensures that they are not just learning concepts but mastering the ability to use them in tangible, real-life situations.
Fostering a Global Perspective:
In a world that is increasingly interconnected, Future-Oriented STEAM Education nurtures a global perspective. Collaborative projects, international partnerships, and exposure to global challenges prepare students to think beyond borders. This global mindset is essential for tackling complex issues that transcend geographical boundaries.
Encouraging Entrepreneurial Thinking:
The future belongs to innovators and entrepreneurs, and Future-Oriented STEAM Education instills an entrepreneurial mindset. Students are encouraged to think creatively, identify opportunities, and develop solutions. This entrepreneurial thinking not only prepares them for potential ventures but also instills resilience and adaptability in the face of challenges.
Cultivating Critical Thinking and Problem-Solving:
Critical thinking is a cornerstone of Future-Oriented STEAM Education. Students are challenged to analyze information, evaluate possibilities, and solve problems independently and collaboratively. These critical thinking skills are not only essential for academic success but are crucial for navigating the complexities of an ever-changing world.
Individualized Learning Paths for Diverse Talents:
Recognizing the diverse talents of students, Future-Oriented STEAM Education adopts individualized learning paths. Whether a student excels in coding, has a passion for design, or leans towards scientific exploration, the curriculum accommodates diverse talents. This personalized approach ensures that each student can harness their unique strengths.
Preparing for Emerging Careers:
Future-Oriented STEAM Education is forward-thinking in its approach to career preparation. It anticipates emerging careers and equips students with the skills and knowledge needed for future job markets. By staying ahead of industry trends, students are prepared for professions that may not even exist today.
Ethical Considerations in Technology:
As technology continues to evolve, ethical considerations become increasingly important. Future-Oriented STEAM Education places a strong emphasis on ethical considerations in technology. Students explore the








