Cutting-Edge Methods: Advancing STEAM Education Excellence
Advancing Excellence in Education: Cutting-Edge STEAM Methods
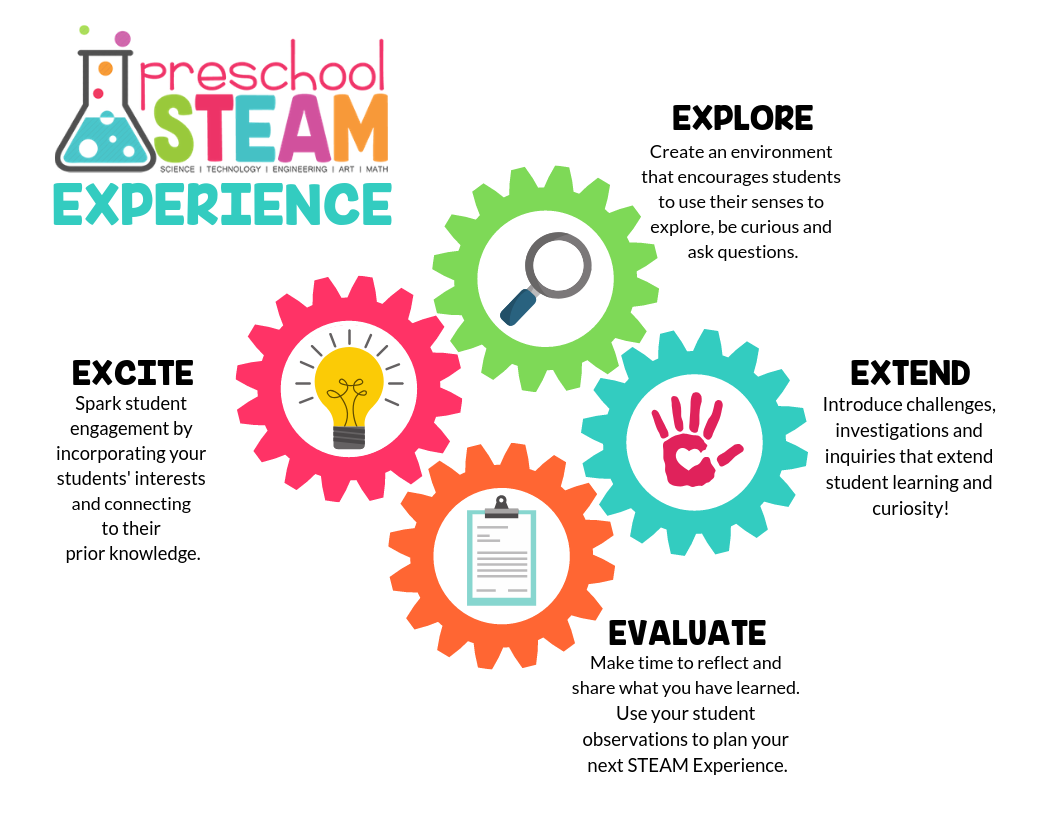
In the ever-evolving landscape of education, staying at the forefront of innovation is paramount. Cutting-edge STEAM (Science, Technology, Engineering, Arts, and Mathematics) education methods are reshaping the way students learn and engage with the world. Let’s delve into the transformative impact of these methods and how they contribute to educational excellence.
Integrating Technology for Immersive Learning Experiences
One key aspect of cutting-edge STEAM education methods is the seamless integration of technology into the learning process. From virtual simulations to interactive online platforms, students experience immersive learning that goes beyond traditional textbooks. This integration not only enhances understanding but also prepares students for a tech-centric future, equipping them with essential digital skills.
Personalized Learning Paths for Individual Mastery
In the era of cutting-edge STEAM education, the one-size-fits-all approach is replaced by personalized learning paths. Adaptive learning platforms analyze individual strengths and weaknesses, tailoring the curriculum to each student’s pace and style. This method ensures that learners can master concepts before progressing, fostering a more comprehensive understanding of STEAM subjects.
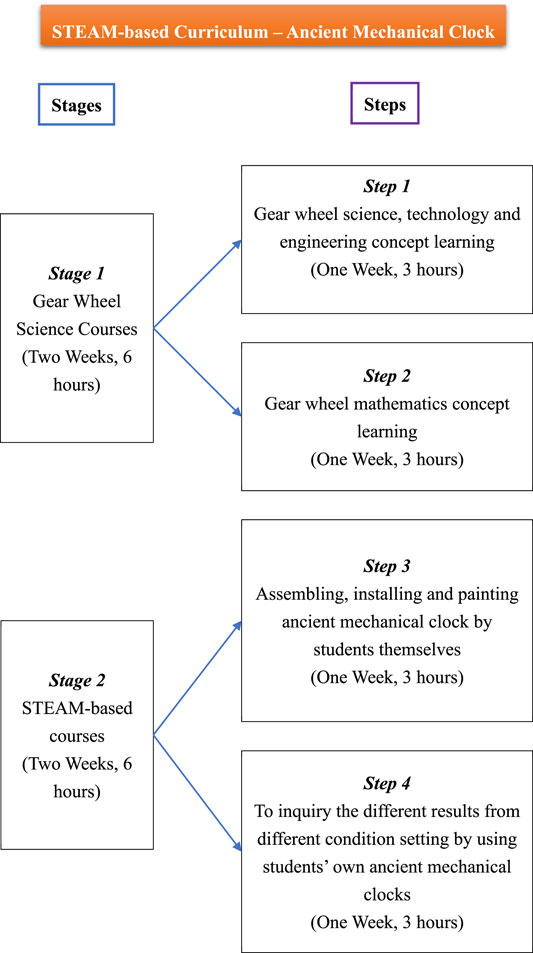
Project-Based Learning: Applying Knowledge in Real-World Contexts
Cutting-edge STEAM education emphasizes project-based learning as a cornerstone method. Students apply theoretical knowledge to real-world scenarios, engaging in hands-on projects that mirror the challenges faced in STEM and arts-related professions. This approach not only reinforces understanding but also cultivates problem-solving skills and creativity.
To explore more about the transformative impact of cutting-edge STEAM education methods, visit www.socialfacepalm.com. This comprehensive resource provides insights, case studies, and tools to support educators, parents, and students on their journey towards cutting-edge learning methods.
Collaborative Platforms for Global Engagement
The advent of cutting-edge STEAM education methods brings with it collaborative platforms that connect students globally. Virtual classrooms and online collaborations break down geographical barriers, allowing learners to engage with peers from different cultures. This global perspective enriches the learning experience, preparing students for a world where cross-cultural collaboration is essential.
Data-Driven Decision-Making in Education
Data analytics play a pivotal role in cutting-edge STEAM education. Educators can track student progress, identify areas of improvement, and tailor interventions based on data insights. This data-driven approach ensures that educational strategies are continually refined to meet the evolving needs of students, fostering a more effective and responsive learning environment.
Incorporating Arts for Holistic Development
While STEM subjects form the core of STEAM education, the inclusion of arts is a distinctive feature of cutting-edge methods. Creative expression through arts enriches the learning experience, fostering a holistic approach to education. This interdisciplinary fusion prepares students for a future where the ability to think creatively and critically is as crucial as technical proficiency.
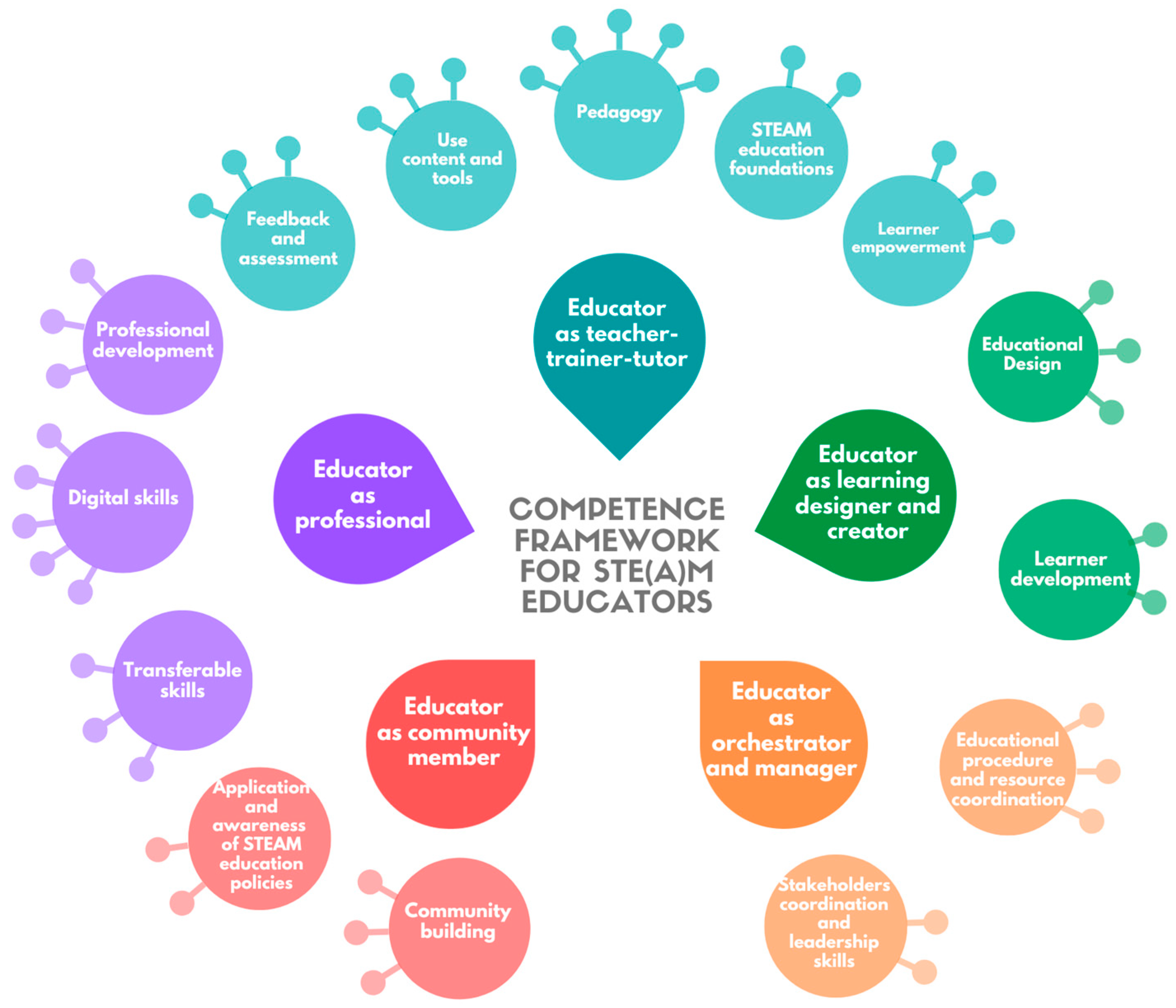
Professional Development for Educators
The implementation of cutting-edge STEAM education methods necessitates continuous professional development for educators. Training programs and workshops ensure that teachers are well-versed in the latest pedagogical approaches and technology tools. Empowered educators, equipped with the knowledge to navigate cutting-edge methods, play a crucial role in shaping the educational experience.
Embracing a Lifelong Learning Mindset
Cutting-edge STEAM education methods instill a lifelong