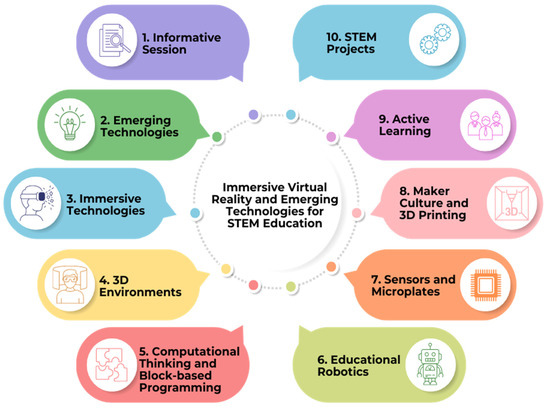
Engaging STEAM Education Activities: Igniting Curiosity and Creativity

Igniting Minds: Exploring the Impact of Engaging STEAM Education Activities
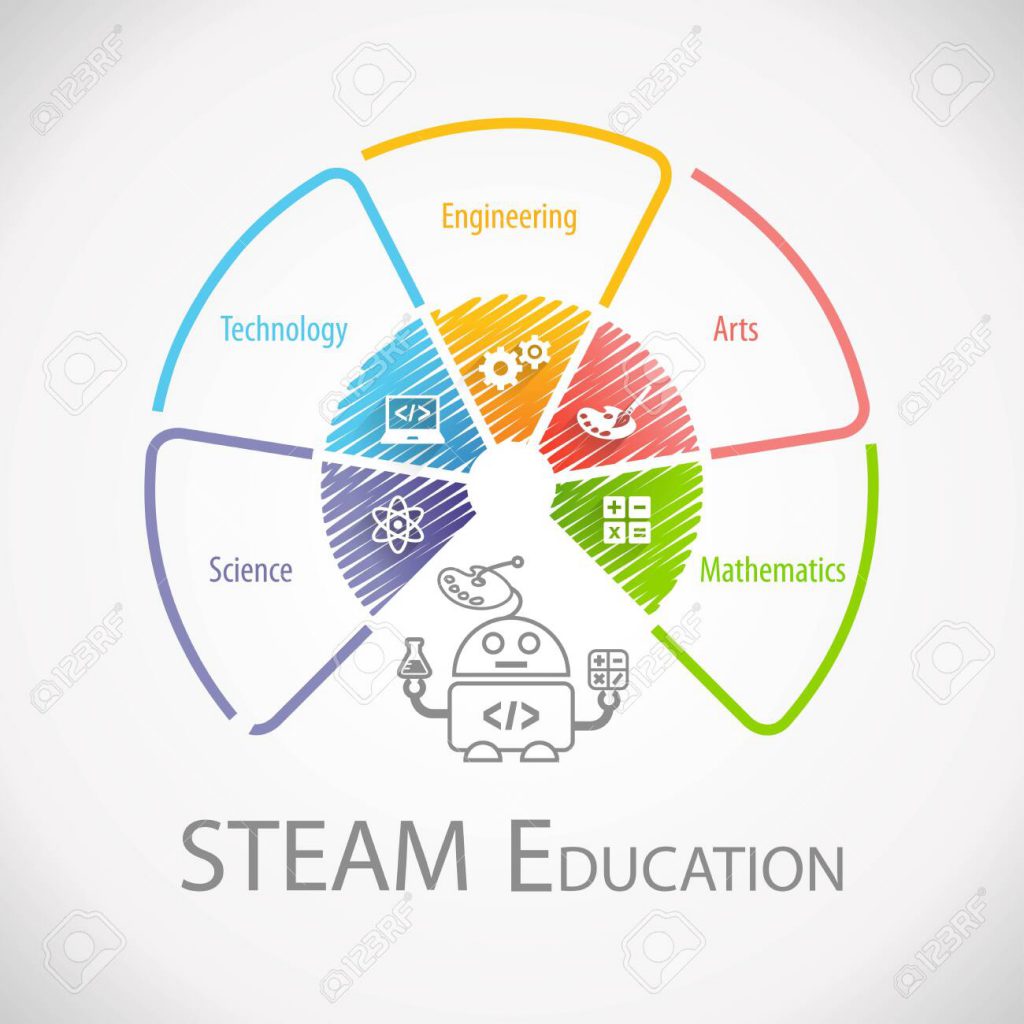
In the realm of education, the integration of Science, Technology, Engineering, Arts, and Mathematics (STEAM) has gained momentum, with a particular emphasis on making learning more engaging and impactful. Engaging STEAM Education Activities have become a driving force in transforming the educational landscape, providing students with dynamic and interactive ways to explore the interconnected world of STEAM disciplines.
Transforming Learning into Exploration:
Traditional education often struggles to capture the attention of students in a way that fosters genuine interest and curiosity. Engaging STEAM Education Activities, however, have successfully transformed the learning experience into an exploration. Through interactive experiments, simulations, and hands-on projects, students delve into the fascinating realms of science, technology, engineering, arts, and mathematics, making learning a captivating journey.
Making Concepts Come Alive:
One of the key advantages of Engaging STEAM Education Activities is their ability to breathe life into abstract concepts. Rather than presenting information in a dry and theoretical manner, these activities immerse students in real-world applications. Virtual labs, experiments, and interactive models allow students to visualize complex ideas, making STEAM subjects more accessible and relevant.
Encouraging Creativity through the Arts:
Incorporating the arts into STEM education is a hallmark of Engaging STEAM Education Activities. The inclusion of creativity through arts not only enriches the learning experience but also encourages students to think outside the box. By connecting the analytical thinking of STEM with the imaginative expression of arts, students develop a holistic skill set that is vital for innovation and problem-solving in the modern world.
Promoting Collaborative Learning:
Engaging STEAM Education Activities go beyond individual achievement by promoting collaborative learning environments. Group projects and interactive challenges require students to work together, fostering teamwork and communication skills. Collaboration becomes a fundamental aspect of the learning process, mirroring the collaborative nature of many real-world STEAM projects.
Fostering a Passion for Inquiry:
Curiosity is the driving force behind meaningful learning, and Engaging STEAM Education Activities are designed to fuel this curiosity. These activities inspire a passion for inquiry, encouraging students to ask questions, explore possibilities, and seek solutions. The emphasis on inquiry-based learning instills a lifelong love for discovery and learning.
Adapting to Diverse Learning Styles:
Recognizing that each student learns differently, Engaging STEAM Education Activities embrace diverse learning styles. Whether a student is a visual learner who benefits from interactive simulations or a kinesthetic learner who thrives on hands-on experiments, these activities cater to various preferences. This adaptability ensures that every student can find a pathway to understanding and success.
Integrating Technology Seamlessly:
In the digital age, technology is a natural companion to education. Engaging STEAM Education Activities seamlessly integrate technology to enhance the learning experience. Virtual reality, augmented reality, and interactive online platforms create immersive environments that captivate students and provide them with tools to explore complex concepts in innovative ways.
Cultivating Critical Thinking Skills:
Critical thinking is a cornerstone of success in STEAM fields, and Engaging STEAM Education Activities prioritize its development. Students are challenged to