Measuring the Momentum: STEAM Education Impact Assessment
Measuring the Momentum: Understanding the Impact of STEAM Education
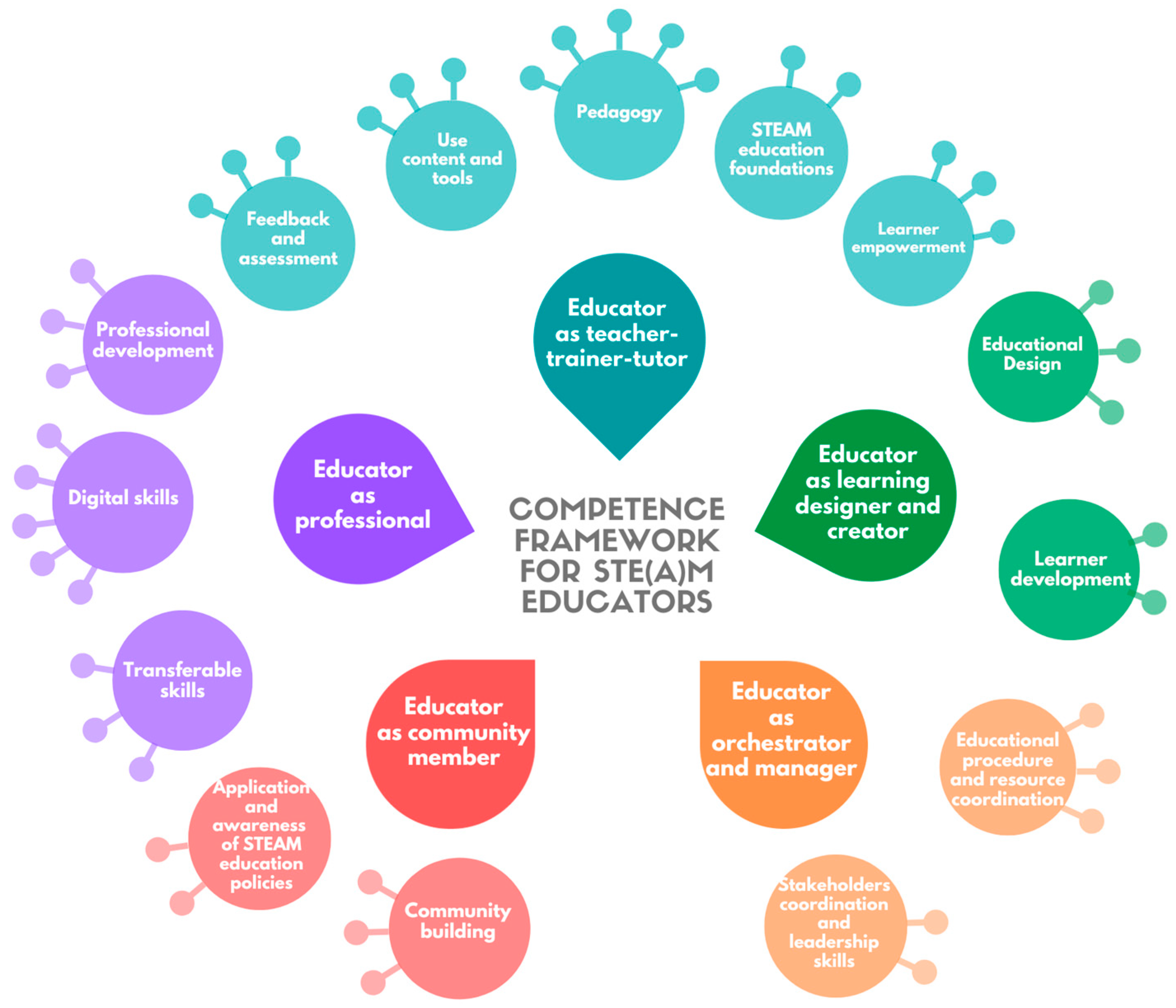
Assessing the impact of Science, Technology, Engineering, Arts, and Mathematics (STEAM) education is crucial for shaping effective learning strategies. This article explores the methodologies and significance of STEAM Education Impact Assessment, shedding light on how educators can measure the effectiveness and success of STEAM programs.
To explore further insights into STEAM Education Impact Assessment, visit www.socialfacepalm.com. This platform serves as a valuable resource for educators and administrators seeking tools and knowledge to assess and enhance the impact of STEAM education.
1. The Holistic Approach to Assessment
STEAM Education Impact Assessment goes beyond traditional measures. It embraces a holistic approach that evaluates not only the acquisition of knowledge but also the development of critical thinking, problem-solving skills, creativity, and collaboration. The holistic nature of assessment aligns with the interdisciplinary goals of STEAM education, reflecting a more comprehensive understanding of student progress.
2. Evaluating Interdisciplinary Learning
One key aspect of STEAM Education Impact Assessment is evaluating interdisciplinary learning. Traditional assessments often compartmentalize subjects, but STEAM programs encourage the integration of multiple disciplines. Assessments in a STEAM context focus on how well students can apply knowledge across various domains, emphasizing the interconnectedness of subjects and real-world problem-solving.
3. Project-Based Assessment Techniques
Project-Based Learning (PBL) is a core component of STEAM education, and assessment techniques align with its principles. Instead of relying solely on exams, educators use project-based assessments to evaluate students’ ability to collaborate, innovate, and apply their knowledge to real-world scenarios. These assessments provide a more authentic representation of a student’s skills and understanding.
4. Assessing Creativity and Innovation
STEAM education places a strong emphasis on fostering creativity and innovation. Therefore, assessment strategies must include methods to evaluate these essential skills. Creative projects, portfolios, and open-ended problem-solving assessments allow educators to gauge students’ ability to think creatively and approach challenges with innovative solutions.
5. Technology Integration in Assessment
Assessment in the context of STEAM education embraces technology. Whether through online platforms, digital portfolios, or coding assessments, technology integration provides efficient and dynamic ways to evaluate students’ technological literacy. Assessments can measure not only technical skills but also the ability to use technology as a tool for learning and problem-solving.
6. Real-World Application Metrics
STEAM Education Impact Assessment is rooted in real-world application metrics. Assessments often include scenarios or projects that mirror authentic challenges students might encounter in their future careers. This approach ensures that students are not just accumulating knowledge but are prepared to apply it meaningfully in professional settings.
7. Student Self-Assessment and Reflection
Encouraging students to actively participate in the assessment process is a unique aspect of STEAM education. Self-assessment and reflection are integral components where students evaluate their own work, identify areas for improvement, and set goals for further learning. This approach fosters a sense of ownership and accountability in the learning process.
8. Long-Term Impact Measurement
STEAM Education Impact Assessment extends beyond short-term results. Educators focus on measuring the long-term impact of STEAM programs on students’ academic and







