Effective STEAM Practices: Transforming Learning Experiences
Revolutionizing Learning: The Impact of Effective STEAM Education Practices
In the dynamic landscape of education, the adoption of Science, Technology, Engineering, Arts, and Mathematics (STEAM) practices has redefined the way students engage with learning. Examining the effectiveness of these practices provides valuable insights into the transformative impact they have on students and the education system as a whole.
Holistic Integration of STEAM Disciplines:
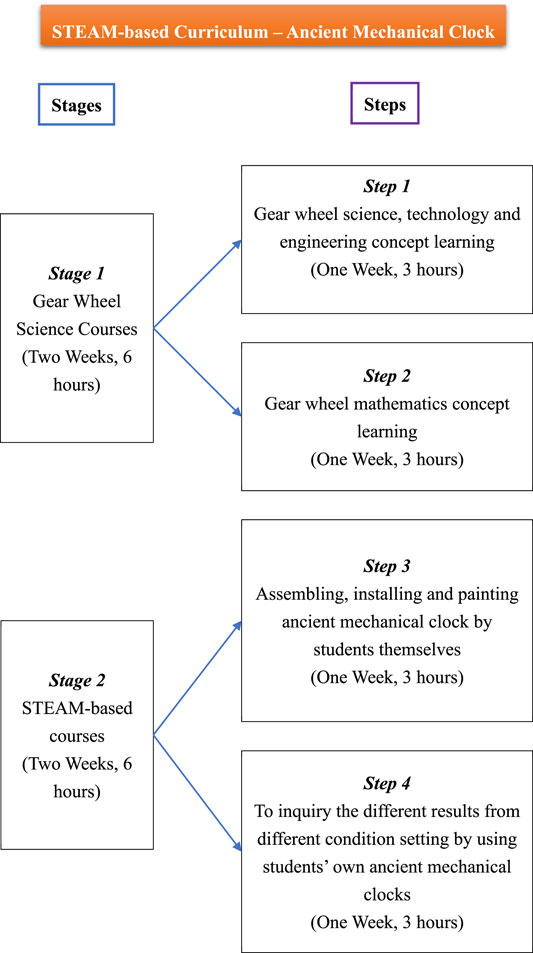
Effective STEAM education practices prioritize the holistic integration of science, technology, engineering, arts, and mathematics. Instead of isolating these disciplines, educators seamlessly weave them together in a cohesive curriculum. This integration fosters a comprehensive understanding of real-world challenges, preparing students for the interdisciplinary nature of the modern workforce.
Hands-On Experiences for Tangible Learning:
At the core of effective STEAM education practices is the emphasis on hands-on experiences. Students actively engage in experiments, projects, and practical applications of their knowledge. These tangible learning experiences go beyond theoretical understanding, providing students with a deeper and more meaningful connection to the subjects they are studying.
Promoting Inquiry-Based Learning:
Effective STEAM practices encourage inquiry-based learning, where students become active participants in their education. Rather than passively receiving information, students are prompted to ask questions, explore concepts, and discover solutions. This approach nurtures a sense of curiosity and instills lifelong learning habits.
Incorporating Project-Based Learning:
Project-based learning is a hallmark of effective STEAM education practices. Students work on projects that mirror real-world challenges, applying their knowledge to solve problems and create solutions. This approach not only enhances academic understanding but also cultivates critical thinking, collaboration, and problem-solving skills essential for success in STEAM professions.
Utilizing Technology as a Tool:
Technology is seamlessly integrated into effective STEAM practices as a tool for learning. From utilizing virtual simulations to coding platforms, technology enhances the educational experience. Students gain not only subject-specific knowledge but also develop essential digital literacy skills, preparing them for the technology-driven demands of the 21st-century workforce.
Encouraging Creative Expression:
Arts integration is a key element of effective STEAM practices. By incorporating creativity into STEM subjects, students are encouraged to think outside the box. Creative expression becomes a powerful tool for problem-solving and innovation. Effective STEAM practices recognize the intrinsic value of fostering creativity alongside analytical thinking.
Fostering a Collaborative Learning Environment:
Effective STEAM education practices prioritize collaboration. Students work together on projects, share ideas, and learn from each other. This collaborative learning environment mirrors the teamwork often required in STEAM professions. It not only enhances students’ social skills but also prepares them for the collaborative nature of future workplaces.
Personalized Learning Approaches:
Recognizing the diverse learning styles of students, effective STEAM practices embrace personalized learning approaches. Adaptive learning platforms and differentiated instruction cater to individual needs, ensuring that each student can progress at their own pace. This personalized approach enhances understanding and retention of STEAM concepts.
Real-World Applications and Context:
Effective STEAM practices bridge the gap between theory and real-world applications. Students are exposed to the practical relevance of their education by applying concepts to authentic scenarios. This connection to real-world