Measuring Impact: Evaluating STEAM Education Outcomes

Measuring the Influence: Navigating STEAM Education Impact Evaluation
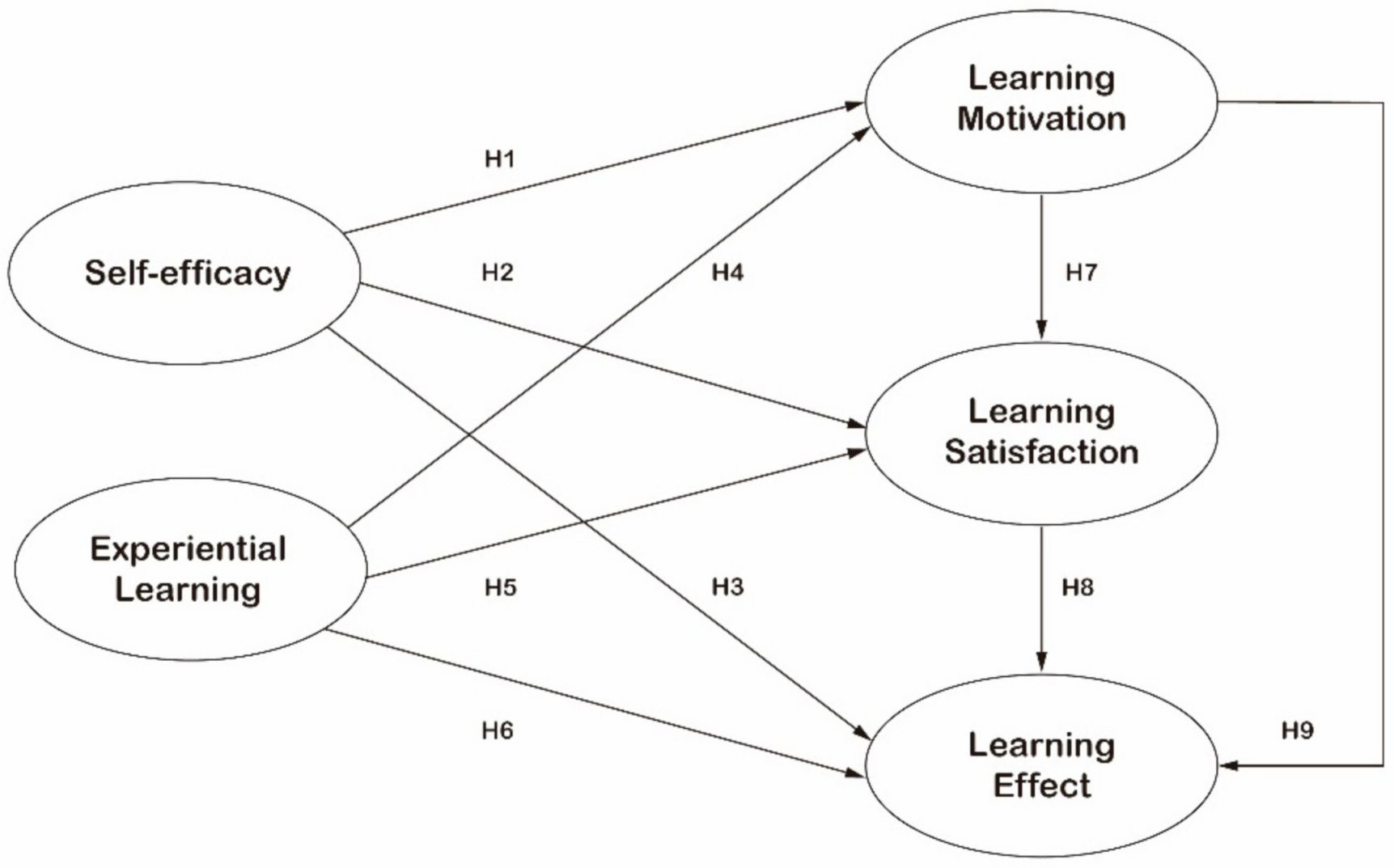
In the dynamic landscape of education, evaluating the impact of STEAM (Science, Technology, Engineering, Arts, and Mathematics) programs is crucial for continuous improvement and effective implementation. This article delves into the methodologies and significance of STEAM education impact evaluation, shedding light on the multifaceted aspects that contribute to its success.
To explore more about STEAM education impact evaluation, visit www.socialfacepalm.com. This comprehensive resource offers insights, case studies, and tools to support educators in navigating the evaluation process and enhancing the impact of STEAM education.
Understanding the Foundations: Defining STEAM Education Impact
Before delving into evaluation methodologies, it’s essential to understand what constitutes the impact of STEAM education. Impact extends beyond academic achievements and encompasses changes in attitudes, skills development, and the ability to apply knowledge in real-world scenarios. Defining these foundations sets the stage for comprehensive evaluation.
Quantitative Metrics: Measuring Tangible Outcomes
Quantitative metrics play a crucial role in STEAM education impact evaluation. These metrics include standardized test scores, grades, and quantitative assessments. Analyzing these tangible outcomes provides a quantitative snapshot of the impact, showcasing improvements in academic performance and subject-specific proficiency.
Qualitative Insights: Unveiling the Intangible Benefits
While quantitative metrics offer a numerical perspective, qualitative insights are equally essential in STEAM education impact evaluation. Qualitative data, such as student interviews, surveys, and observations, unveils the intangible benefits. This includes increased creativity, improved problem-solving skills, and enhanced collaboration—an invaluable dimension of the overall impact.
Long-Term Impact Assessment: Beyond Immediate Outcomes
STEAM education’s impact is not confined to immediate outcomes. Evaluating the long-term impact involves tracking students’ progress beyond the educational setting. This could include their pursuit of STEAM-related careers, continued engagement in STEM projects, or contributions to innovative endeavors. Long-term assessments provide a holistic view of the enduring impact of STEAM education.
Assessing Teacher Effectiveness: A Key Component
Teachers play a pivotal role in the success of STEAM education initiatives. Evaluating the impact of STEAM education involves assessing teacher effectiveness. This includes their ability to inspire students, implement innovative teaching methods, and adapt to evolving educational needs. Effective teacher evaluation is integral to sustaining positive impacts on students.
Student Engagement Metrics: Gauging Interest and Participation
One of the indicators of STEAM education impact is student engagement. Metrics such as participation rates, attendance, and enthusiasm in STEAM-related activities provide insights into the level of engagement. High levels of student engagement are indicative of a positive impact, as students actively involve themselves in the learning process.
Parent and Community Involvement: Assessing External Support
Beyond the classroom, the impact of STEAM education extends to parents and the community. Evaluating the involvement of parents in STEAM initiatives and community support for STEM events is crucial. This external engagement contributes to a supportive ecosystem that enhances the overall impact of STEAM education.
Continuous Program Improvement: The Role of Feedback
STEAM education impact evaluation is not a one-time process; it’s an ongoing journey. Incorporating feedback mechanisms allows for continuous program improvement. Gathering input from students, teachers, parents,