Higher Education Compliance Alliance
 For students, the panic button goes off once they get an admission to the college of their dream. As seen above, institutions of higher studying will not be proof against shifts to exterior components such as those explored by means of the S.T.E.E.P. analysis; specifically, socio-cultural, technological, environmental/ecological, economic, and or political circumstances.
For students, the panic button goes off once they get an admission to the college of their dream. As seen above, institutions of higher studying will not be proof against shifts to exterior components such as those explored by means of the S.T.E.E.P. analysis; specifically, socio-cultural, technological, environmental/ecological, economic, and or political circumstances.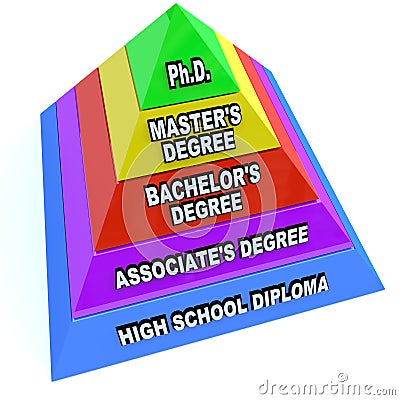
We need to move beyond thinking of educational freedom solely as a unfavorable liberty that is fundamentally individualist in nature (where the problem revolves round censorship), and suppose seriously in regards to the accountable exercise of the right as a type of shared governance in increased education.
The recording from the 2015 session may be discovered here The VIS offers a possibility for current faculty to explain the HESA doctoral program to potential doctoral college students as well as enable the opportunity for potential students to ask questions pertaining to the program.
To strengthen strategic collaborations between native and international higher education establishments, as well as famend native and international establishments in the discipline of analysis, growth and commercialisation. Nevertheless, in line with Thorndike extra play a job in education is that it gives an award or reward and that’s what is recommended. The common financing strategies for larger education are; savings, bank loans, borrowings from households and pals and sponsorship from the public e.g. although use of CDF. Discussion surrounding it is going to continue to be related as political campaigns will proceed to focus on education.
All have demonstrated the potential to be excellent professionals who can assume management positions in many alternative areas of upper education and can be collaborative practitioners facilitating change and innovation. To develop academicians of higher educational establishments who possess excessive scholastic skills to excel in their respective specialised fields of specialisation.…






